Atrial Septal Defect
As the name implies an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a hole in-between the two atria, the most common form of which is through the septum secundum.
Obviously the symptoms a patient experience is dependent on the size of the defect.
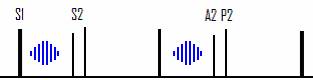
Classically there is S2 splitting as the pulmonary valve closure (P2) occurs later due to increased blood flow through the system. This splitting will remain constant and not vary with respiration as the defect effectively equalises out any differences respiration would cause. (Unlike physiological splitting)
The extra pulmonary flow causes a mid-systolic pulmonary flow murmur.